This is the second article in a series to explain why Penang State Government should review the Penang Transport Master Plan (PTMP).
ANALYSIS | Not many people realise how distorted the current version of the PTMP undertaken by a Gamuda-led corporate consortium is from the original PTMP adopted by the Penang state government in March 2013.
The original, prepared by renowned UK-based engineering consultant Halcrow, aims for a holistic approach to solving Penang’s mobility and transport problems, adopting a paradigm shift by moving people - not cars. It aims to make roads safe and user-friendly for all, especially pedestrians, cyclists and the physically disadvantaged. Crucially, it envisages the building of a tunnel and more highways only as longer term priorities if required.
However, after SRS Consortium Sdn Bhd - a joint-venture between Gamuda Bhd (60 percent) and local real estate development firms Loh Phoy Yen Holdings Sdn Bhd (20 percent) and Ideal Property Development Sdn Bhd (20 percent) – took over, the PTMP was revamped to deviate substantially from the Halcrow plan.
Instead of implementing the original strategies, the state turned its focus towards megaprojects that led the cost of the SRS proposal to balloon to a mind-boggling RM46 billion.
Perplexingly enough, the SRS plan ignored all the institutional and short and medium-term measures of the Halcrow plan, and only focussed on adding more mega-infrastructures and highways. For the public transport system, SRS ditched Halcrow’s recommended BRT (bus rapid transit) and tram for a monorail and an LRT. This was despite the monorail being an outdated technology and hardly used anywhere in the world as a means of public transportation. Sydney and Moscow have torn down their monorail systems.
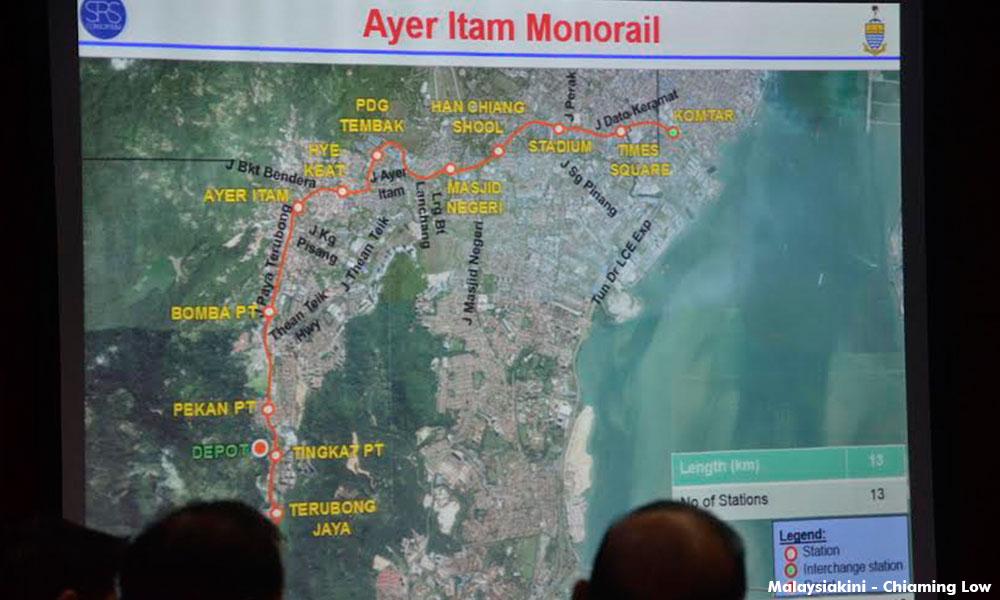
Even former chief minister Lim Guan Eng had stated on March 15, 2013 that “BN’s monorail is inappropriate for a world heritage city like Penang, as its elevated structure will destroy Penang’s charms.” The same can be said for the proposed LRT.
Another factor to note is that the selection of SRS as the project delivery partner (PDP) to implement the PTMP was not based on an open tender system, but through a Request-for-Proposal (RFP).
In an open tender, a client that calls for a tender defines the project with detailed specifications. Parties that submit tenders must then conform to the specifications so that the cheapest tender can be selected. However, in a RFP, the tenderers submit different proposals to the client. No two proposals submitted under an RFP are similar, and therefore they cannot be compared. The procurement and negotiation processes thus become more prone to rigging or abuse.
Having opted for the RFP, the state government called for bidders in August 2014 and received a total of six bids by the closing date in February 2015. This eventually led to the state awarding the project to SRS Consortium in August 2015. As a PDP, the consortium’s role is to manage the implementation of the master plan and guarantee its timely and acceptable completion for a fee (in this casem six percent of the total project cost).
Curiously, the state also allocated RM305 million just to do the feasibility and detail design studies for the undersea tunnel and three highways on Penang island. The MACC is investigating these matters.
The Halcrow plan’s holistic agenda
A principal objective of the original PTMP was to increase public modal share of transport from five percent to 40 percent in twenty years (2011 to 2030). To achieve this, a series of short, medium and long-term steps were proposed, through four strategies:
- Make better use of the state’s existing roads and transport networks;
- Strengthen institutional capabilities;
- Have proposals to provide additional highway and public transport infrastructures only for the longer term; and
- Institute traffic management policies aimed at reducing further growth of private vehicle activity.
Steps (1) and (2) call for:
- Improving regulation and enforcement against illegal waiting, parking, loading and hawker activities;
- Better management of on-street parking control regime;
- Reorganising existing bus networks into a series of core and secondary bus routes, plus feeder bus routes to serve residential and industrial communities;
- Changing the way development applications are approved by moving away from Traffic Impact Assessment, which has failed, to a system based on transport-related development contributions and better audit of transport accessibility.
In terms of public transport, the original PTMP talks of upgrading existing bus services to BRT services or tram services. Nowhere did the plan recommend monorails and LRT.

To help public transport take off, it emphasised the need to significantly improve pedestrian accessibility in terms of shaded walkways integrated with bus stops and buildings. Clearing of five-foot walkways is a priority so that pedestrians can walk comfortably and safely. Not much expense is necessary to achieve this.
Interestingly, the Halcrow plan also recommends improving the ferry services and introducing other water transport services to link George Town to the northern and southern coasts of the state. The consultants cautioned that this might be difficult if the state does not have the support of the federal authorities. But now that Pakatan Harapan has control over the state and federal agencies, this should no longer be a stumbling block.
It is alarming that the SRS version of the PTMP significantly detracts from the above. What happened to funding for institutional reforms, pedestrian and cycling infrastructures, water transport and feeder buses that constitute the necessary elements for a holistic and balanced transportation system?
Something has gone terribly wrong.
READ MORE
Part 1: Relooking the Penang Transport Master Plan
Part 3: Was the Penang Transport Master Plan awarded with open tender?
Part 4: Why bulldoze through Penang undersea tunnel project?
Part 5: Why Penang’s expensive LRT plan must be reviewed
Part 6: Why an independent review of the SRS-proposed PTMP is needed
AHMAD HILMY is an associate professor at Universiti Sains Malaysia, while LIM MAH HUI is a former professor, international banker and Penang city councillor.
The views expressed here are those of the author/contributor and do not necessarily represent the views of Malaysiakini.

